Readily available cloud resources have led to significant changes in the technological landscape, and the hybrid cloud approach has become increasingly popular among organizations such as Netflix, Hulu, Uber, and Airbnb. This approach adopts high-performance and lower-cost cloud technologies while offsetting security and compliance concerns with on-premises and private cloud resources. However, the hybrid nature of this approach demands extensive communication and coordination for optimal operation. A lack of safety measures for this communication can give rise to vulnerabilities and challenges, particularly regarding overall security.
Hybrid cloud security encompasses technologies and strategic approaches designed to safeguard your data, applications, and resources in the dynamic context of a hybrid cloud environment. This comprehensive approach addresses multifaceted challenges, including data protection, identity and access management, network security, compliance, and regulatory adherence, as well as seamless integration and interoperability considerations.
This article delves into the challenges posed by hybrid cloud security and explores the best practices for its use. It also introduces some essential tools and methodologies to ensure the safety of your architecture.
Common Challenges with Hybrid Cloud Security
While a hybrid cloud framework has the potential to significantly enhance organizational effectiveness and performance in alignment with your goals, it also comes with various security concerns. These concerns arise from the combination of resources located off-premises and the need for smooth integration and interaction between on-premises, private cloud, and public cloud resources. The following are some common challenges you may encounter if you use hybrid cloud security in your infrastructure.
Data Protection
Data protection is a significant hurdle in hybrid cloud security. Safeguarding your data as it moves between on-premises and cloud environments, both at rest and during transit, presents a multifaceted challenge. This process requires safety measures for your data as it’s being transmitted and processed, as well as at the producing and receiving ends of the process. This task is complicated by varying encryption practices and key management among different cloud providers.
The dynamic nature of a hybrid cloud setup, with its need for frequent movement and interaction between on-premises and cloud platforms, adds further complexity. For example, Netflix uses a hybrid cloud storage solution that combines Amazon Web Services (AWS) and on-premises storage. This kind of setup requires consistent encryption and real-time monitoring to ensure data remains secure at all stages and to prevent critical vulnerabilities during data migration. Leading corporations like Netflix employ a blend of native cloud service provider (CSP) solutions, third-party tools, and proprietary in-house innovations to counter security threats and protect their data.
Identity and Access Management
Within your organization, you’ll have multiple individuals with varying levels of access, and a hybrid cloud environment requires multiple authentication mechanisms and authorization protocols across your on-premises and cloud environments. Managing user identities, roles, and access rights becomes complex when you need to ensure consistent access controls during the movement of users and resources between environments. This challenge increases as your organization grows, with larger organizations like Netflix needing to provide secure access for hundreds of employees while also limiting proprietary information from public eyes.
Network Security
A robust and secure network connection is central to effective hybrid cloud operations, as it affects communication and coordination within your environment. Securing network communications and maintaining visibility and control over the data flowing between on-premises and cloud environments presents a critical challenge in hybrid cloud security. This involves ensuring adequate monitoring throughout your network, addressing potential vulnerabilities, and establishing consistent protection against unauthorized access and data breaches across the interconnected domains.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
When working with confidential information or personal data in general, there are specific regulations about how data should be processed and stored. Adhering to these requirements can be particularly challenging in hybrid cloud deployments where you have to work on two frontiers (on-premises and cloud platforms) that must align. You have to be sure your data storage, processing, and transmission practices on- and off-premises meet industry specific regulations like PCI DSS or HIPAA. You must ensure that your hybrid cloud environment and the cloud providers used meet the stringent requirements imposed by these regulations, encompassing data privacy, security, and handling.
Data Governance and Sovereignty
Your organization may face various challenges when ensuring sensitive data complies with regional policies during storage and processing. The complexity of this task arises from having to manage data governance and sovereignty consistently across diverse segments of your hybrid cloud infrastructure, all while aligning with both regulatory requirements and internal protocols.
For example, this includes addressing data residency requirements such as the GDPR, which mandates that data related to EU citizens or residents must be collected, processed, and stored within the borders of the EU.
Cloud Provider Security
The primary challenge here lies in finding a cloud service provider whose security practices and policies you can trust. The considerations in choosing a cloud provider are not limited to the effectiveness of their service but also involve assessing the security measures employed by these providers, encompassing aspects like data isolation, vulnerability management, and incident response capabilities. You must evaluate the level of security these providers offer to ensure your hybrid cloud environment remains resilient against potential threats and breaches, striking a balance between leveraging external expertise and maintaining a zero trust security stance. This involves researching CSP information on cloud security, for example, Amazon Web Services, exploring case studies of companies who have used these services, and making a decision based on how suitable the CSP services are to your infrastructure.
Integration and Interoperability
Another major challenge when dealing with a mixture of on-premises systems and cloud environments is ensuring secure communication and seamless integration within your entire infrastructure. You need to implement secure APIs for your various services and establish consistent interoperability between them. Integrating identity management systems and ensuring the safe integration of data are also important considerations. Each service or system added to your environment has to be in harmony with the others to guarantee a cohesive and secure environment for efficient collaboration between on-premises and cloud resources.
Cloud Sprawl and Shadow IT
In general, managing and monitoring hybrid cloud deployments can be a challenging task requiring manpower and skill. Cloud sprawl and shadow IT are two consequences of an improperly managed deployment. Cloud sprawl occurs when organizations lose visibility and control over their various cloud instances. Shadow IT occurs when individual employees use various cloud services and applications (such as cloud storage, messaging software, or management tools) that are unauthorized or without the approval of the IT department, leading to security risks.
Hybrid Cloud Security Best Practices
In this section, you’ll explore methods of addressing the previously stated challenges and best practices for establishing a strong hybrid cloud security foundation, including comprehensive security strategies, robust identity management, network segmentation, thorough provider evaluation, vulnerability management, and proactive monitoring.
Comprehensive Security
A comprehensive security strategy is the foundation of your infrastructure’s security. Your strategy should be tailored to the features of your on-premises and cloud domains and align with your organization’s distinct security requirements, compliance regulations, and pertinent industry benchmarks.
Data Classification and Protection
If your infrastructure generates a lot of peripheral and nonsensitive data that is still processed and stored, segmenting your data is a good idea. This involves classifying your data according to its sensitivity and applying specific security measures to each segment. This process allows you to implement strong encryption (at rest and in transit), access controls, and data loss prevention measures for your most sensitive data without impeding data processing for your whole system. For example, you could have financial, health, and nonconfidential HR records in your infrastructure. Being able to segment highly sensitive documents and less important files will help with managing overall security and the time and performance costs of stringent security.
Prioritize Identity and Access Management
Identity and access management (IAM) is central to the security of your infrastructure and should be prioritized in your strategy. Implement robust IAM practices to ensure proper authentication, authorization, and access control. Establish multifactor authentication (MFA) for your user accounts and enforce least privilege principles to grant access only when necessary.
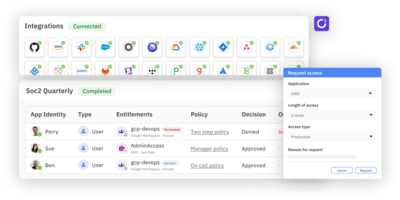
Consistently monitor, review, and revoke access privileges for employees and third-party users to ensure the security of your infrastructure is maintained. Advanced access management tools such as ConductorOne can help you with tailored features for automating access reviews and providing just-in-time (JIT) access for your user accounts and cloud resources.
Network Segmentation and Firewalls
In implementing zero trust, network segmentation can be used to isolate sensitive resources and restrict access to them. Segment your network into zones or subnets based on trust levels and establish firewalls between them. You can create granular security policies that apply to specific users, devices, or applications. This helps contain security breaches and limits the lateral movement of attackers within the hybrid cloud environment.
Cloud Provider Evaluation
Evaluate the cloud service providers (CSPs) you use or allow into your hybrid environment, and opt for CSPs that prioritize security and compliance. Check the security certifications of your CSPs, their data privacy rules and policies, how they handle security incidents, and how they encrypt data. Set clear roles and expectations with your CSP regarding security controls and how you will collaborate to handle security incidents within your environment.
Vulnerability Management
Maintaining a secure hybrid cloud ecosystem requires vigilant monitoring and the expedited mitigation of vulnerabilities. Vulnerability management is the ongoing process of finding security risks in your on-premises and cloud platforms, reporting them, and fixing them. Implement a comprehensive vulnerability management process with regular vulnerability assessments and patch management for your infrastructure. Monitor potentially vulnerable areas and explore remediation options in case of an incident. This will help you tackle and fix vulnerabilities in a timely manner.
Tools such as ConductorOne can help mitigate security vulnerabilities related to orphaned and unused access by identifying and remediating unused access or deactivated accounts. They can also force access renewals after a period of time, which is especially important for sensitive access.
Security Monitoring and Logging
Extensive monitoring and logging of your infrastructure improves your ability to investigate security incidents and respond to issues in a timely manner. Utilize reliable and extensive monitoring and logging mechanisms to quickly and effectively identify and address security incidents. You can centralize your generated logs from both on-premises and cloud systems to attain holistic visibility within your environment. Simplify the process of analyzing and correlating security events by using security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
Incident Response and Forensics
Security attacks have become more common in recent times, so it’s important to explore how your organization should react after a cyberattack. Formulate a tailored incident response plan designed for your hybrid cloud environments. Define escalation protocols, establish defined roles and duties, and do frequent incident response drills. Make sure the necessary forensic tools are available to look into security issues
Regular Audits and Compliance
Regular reviews and audits are needed to assess the effectiveness of your implemented systems, identify gaps and weaknesses, and verify consistent compliance with organizational and industry regulations. You can engage third-party auditors to provide an independent evaluation of your security posture. ConductorOne helps you improve your security posture and reduce security risk with a central platform for your identity governance and access controls. You can ease your review process with automated compliance audits and reports.
Continuous Improvement
No security profile is perfect; there are always improvements to be made as technology advances and becomes more complex. It’s important to keep up with the latest security improvements, risks, gaps, and best practices in hybrid cloud security. Foster an ongoing cycle of assessment and enhancement for your security framework, embracing new technologies, adopting emerging security solutions, and drawing insights from security incidents to fortify your overall security posture.
Conclusion
In this article, you explored the challenges involved in ensuring a secure hybrid cloud environment, including data protection, access management, network security, and compliance adherence. To address these challenges, this article also walked you through some best practices for your hybrid cloud security, such as robust identity management, network segmentation, thorough cloud provider evaluation, and proactive monitoring.
ConductorOne is a pioneering authority in identity security and access governance. It empowers enterprises to streamline user access to cloud and on-prem applications and infrastructure. By leveraging ConductorOne, businesses can automate and orchestrate processes through access reviews, self-service requests, just-in-time provisioning, and offboarding workflows.