Modern organizations face an expanding landscape of risks driven by cloud sprawl, rising regulatory pressure, and the explosive growth of AI and non-human identities. GRC platforms in 2026 must deliver more than simple reporting. They must unify risk, compliance, and identity governance in one place, automate the work, and provide real-time visibility that keeps teams ahead of threats.
This updated 2026 guide highlights the leading GRC and identity security solutions available today. It explains their top features, advantages, limitations, and ideal use cases. It also shows how AI-driven automation, continuous monitoring, and unified identity governance are reshaping the market for modern enterprises.
Whether you are evaluating a new GRC platform or upgrading from a legacy system, use this guide to compare the leaders and choose the tool that matches your organization’s scale, compliance requirements, and automation needs.
1. ConductorOne
The Leading AI-Native Identity Security and Access Governance Platform in 2026
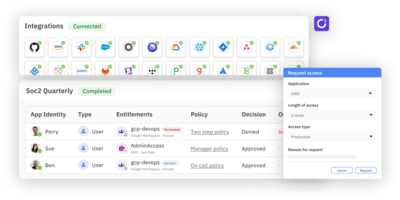
ConductorOne is the most advanced AI-native identity governance and access management platform that centralizes and automates access management across cloud and on-prem applications and infrastructure.
It helps organizations secure all human and non-human identities, automate access governance, and enforce least privilege at scale. The platform unifies provisioning, user access reviews, lifecycle management, and policy-based access controls into one modern system that works across cloud and on-prem environments.
ConductorOne is built for companies with rapidly growing identity footprints. Its multi-agent AI engine automates the work that previously required large IGA teams, making it possible to manage identity governance with speed, precision, and continuous compliance.
Updated 2026 Capabilities
Autonomous Governance Engine (AGE). ConductorOne’s AI-powered governance engine uses multiple specialized agents to automate provisioning, access reviews, role insights, and policy decisions. AGE analyzes identity patterns, flags toxic access combinations, identifies unnecessary permissions, and recommends cleanup actions.
AI Agents for Access Requests and User Access Reviews. AI agents evaluate access requests using role context, historical approval patterns, separation of duties rules, and risk scoring. They can auto-approve low-risk requests, escalate edge cases, and provide human-readable explanations for every decision.
Super Directory for Identity Orchestration. Super Directory provides a single source of truth across humans, service accounts, SaaS apps, infrastructure, and AI agents. It aggregates identities from HRIS, cloud providers, directories, and custom systems while enriching them with dynamic attributes for smarter policy decisions.
Best-in-Class Integrations. ConductorOne ships with hundreds of high-fidelity connectors, including connectors built for AI services, internal tools, legacy systems, and cloud infrastructure. Connectors support continuous sync, deep entitlements, and real-time updates.
Watch now: C1 Connectors: Connect Every App
Lifecycle Automation Across the Identity Surface.
Joiner, mover, and leaver workflows run automatically based on HRIS signals, identity attributes, and business rules. AI agents detect anomalies like missing access or overprovisioned identities and trigger fixes without waiting for manual intervention.
Intelligent Access Reviews.
AI-powered UARs reduce reviewer fatigue by grouping similar decisions, flagging unnecessary access, and pre-recommending removals. Review cycles that once took weeks now take minutes.
Top Features
- Self-Service Access Requests. Provides a centralized interface for users to request access to resources across all integrated systems. The portal displays available resources based on each user’s role and permissions, simplifying the request process. Approval workflows are also automated, allowing managers to review requests quickly while ensuring that requests are consistent with organizational access policies.
- Automated Access Reviews. Automates user access reviews, notifying managers to review and confirm each user’s access rights. This ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and minimizes the risk of privilege creep by maintaining only necessary permissions.
- Dynamic Access Controls. Allows administrators to define granular access policies based on specific roles, groups, or attributes. These policies automate access provisioning and deprovisioning, ensuring that permissions are assigned only when they meet predefined criteria. The policy engine supports fine-grained controls that allow organizations to enforce least-privilege access principles.
- Compliance and Audit Reporting. Provides detailed logs of user activities, access requests, and approvals, enabling organizations to meet regulatory requirements for access management and maintain a clear audit trail. The platform generates customizable compliance reports that can be tailored to meet the needs of different frameworks, such as SOC 2, HIPAA, or GDPR.
What Makes ConductorOne Different?
- User-Friendly Access Request Interface. With a straightforward, self-service interface, ConductorOne allows users to request and manage access via web app, Slack, or CLI without overburdening IT staff. This helps employees gain access when needed without complicated or delayed processes.
- Seamless Integration with Existing Tools. ConductorOne offers robust integrations with a wide range of cloud applications, IT infrastructure, and on-premise systems, including homegrown and private systems and popular platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, Okta, and Microsoft Azure. This integration capability allows organizations to manage access permissions across their entire environment, ensuring that access governance policies are applied consistently throughout the IT ecosystem.
- Automated Access Control. ConductorOne emphasizes a zero-touch automation model, which helps businesses reduce manual intervention but also ensures faster, more secure provisioning and deprovisioning of user access. This feature stands out in companies where complex workflows and multiple approval layers typically slow down access control.
- Fine-Grained Permissions Management. ConductorOne enables precise control over permissions, allowing IT teams to define and enforce policies down to specific roles and entitlements. This level of granularity helps organizations avoid over-provisioning, minimizing security risks associated with excessive permissions.
Why Do Companies Choose ConductorOne?
Picture this: You’re managing hundreds of employees across different departments, each needing access to dozens of applications.
Without proper governance, it’s a recipe for security nightmares – from forgotten access revocations to compliance violations. That’s where ConductorOne comes in.
Companies choose ConductorOne for GRC because it automates the tedious parts of identity security while keeping them compliant.
Pricing
- Contact ConductorOne for more information.
2. SAP GRC
SAP GRC is an integrated suite of tools that organizations use to manage risk, ensure compliance with regulations, and establish robust governance frameworks.
It integrates with SAP ERP and other SAP products, making it a powerful tool for organizations already leveraging SAP’s ecosystem. The suite includes modules for risk management, audit management, access control, and business integrity screening, among others.
The platform automates regulatory compliance processes, helping businesses stay updated with current regulations and minimize manual efforts involved in audits and assessments.
For example, SAP GRC’s real-time monitoring capabilities track policy violations, unusual access patterns, and other potential risks across SAP and non-SAP applications.
In addition, SAP GRC’s modular structure enables companies to implement only the components they need, allowing for customized governance and compliance solutions that meet specific organizational requirements.
Top Features
- Access Control. Automated user provisioning, enforces SoD rules, and monitors access requests for policy violations.
- Process Control. It supports real-time control monitoring, control assessments, and policy violation tracking, helping organizations manage risks and maintain compliance with industry regulations. The feature also supports automated testing and documentation, making audit preparation faster and more efficient.
- Risk Management. Allows users to define risk categories, set risk tolerance levels, and create action plans for risk mitigation.
- Fraud Management. Employs predictive analytics and rule-based logic to identify anomalous patterns in transaction data, reducing the likelihood of financial and reputational losses.
Advantages
- 3. Unified Process Control. The platform delivers on its name by comprehensively managing company compliance, process control, risk management, and user access in one system [*].
- Advanced Integration Capabilities. Easy-to-use interface provides comprehensive risk control and user access management, with ability to integrate with other systems like Oracle [*].
- Streamlined Authorization Management. The ability to check authorization status and copy roles between users enhances efficiency, while providing comprehensive organizational risk assessment capabilities [*].
Disadvantages
- Performance Issues. System suffers from significant slowdowns and delayed responses, requiring extensive RAM and space while increasing processing time [*].
- Role Discovery Challenges. The system lacks intuitive role search functionality, making it difficult to identify needed roles without prior knowledge of the organization’s specific role structure [*].
- Implementation Challenges. Requires deep technical knowledge of SAP Basis and Security, while high costs and complexity make it unsuitable for smaller organizations [*].
Pricing
- Contact SAP for more information.
3. Resolver
Resolver is a cloud-based risk management software designed to streamline and enhance the processes of incident management, risk assessment, internal audit, compliance, and IT risk management.
The platform provides organizations with a centralized solution to identify, evaluate, mitigate, and monitor risks— all in real time. Resolver integrates with existing systems and offers a flexible approach to GRC by allowing organizations to configure workflows, customize risk assessments, and automate reporting based on their specific needs.
In addition to risk and incident tracking, Resolver includes advanced analytics and data visualization tools, providing detailed insights into risk levels, compliance gaps, and control performance. The platform’s configurable dashboards and reporting capabilities enable organizations to keep stakeholders informed and ensure that decision-making is based on up-to-date risk intelligence.
Top Features
- Incident Management. Offers automated workflows for reporting, escalation, investigation, and resolution, with features that allow organizations to log incident details, assign ownership, and track corrective actions.
- Compliance Management. Automates compliance processes, tracks regulatory updates, and provides real-time compliance monitoring.
- Internal Audit Management. Allows organizations to conduct risk-based audits, automate audit workflows, and track findings to resolution. It also includes collaboration capabilities, enabling teams to communicate audit findings and track corrective actions in real time.
- IT Risk Management. Enables businesses to identify, assess, and mitigate vulnerabilities associated with IT systems and infrastructure
- Configurable Dashboards and Workflow Automation. Allows users to view relevant metrics, while automated workflows streamline routine tasks, such as incident escalation, compliance monitoring, and audit tracking.
Advantages
- Portal Customization. The platform offers extensive customization capabilities for templates and portals, allowing departments to tailor the system to their specific needs with easy reporting functionality [*].
- Seamless Implementation Process. Despite the complexity of SaaS deployments, the platform offers smooth implementation with superior customer support and efficient security incident tracking [*].
- User-Friendly Interface & Integration. Clean UI design with straightforward application creation and form building, enhanced by effective dashboards and easy API integration [*].
Disadvantages
- Configuration Complexity. Despite unlimited customization options, users find it challenging to locate specific screen or field customization settings [*].
- Role & Report Management Issues. Building and maintaining roles and reports proves more complex than basic form and workflow management [*].
- Complex Learning & Licensing. Steep learning curve due to system’s architecture, complicated by an unnecessarily complex licensing model [*].
Pricing
- Contact Resolver for more information.
4. MetricStream
MetricStream is a leading provider of GRC solutions designed to help organizations streamline and automate their enterprise-wide GRC programs.
MetricStream’s core offering is the ConnectedGRC suite, which provides a comprehensive set of applications to manage various aspects of GRC:
- BusinessGRC. Focuses on enterprise and operational risk management, policy and compliance management, and third-party risk management.
- CyberGRC. Addresses IT and cybersecurity risk management, IT compliance, and cyber policy management.
- ESGRC. Supports environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives by managing sustainability risks and compliance.
Top Features
- AppStudio. A low-code development environment that allows users to configure and extend MetricStream applications to meet specific business requirements.
- Federated Data Model. Provides a centralized data model with predefined relationships across risks, regulations, assets, controls, organizational entities, processes, and issues, ensuring a single source of truth for real-time, risk-aware decision-making.
- Continuous Control Monitoring (CCM). Automates evidence collection at scale, offering total coverage compared to limited sampling in manual assessments, thereby enhancing efficiency and accuracy in compliance processes.
- Multi-Dimensional Organization Structure (MDOS). Enables mapping of corporate hierarchy, geographies, and business units to risk and compliance information.
Advantages
- Flexible Risk Assessment. Provides excellent IT risk management visibility with adaptable scoring systems and easy integration of company-specific factors [*].
- Professional Integration Support. Qualified professional team effectively translates client needs into easily implementable and integrated models [*].
- Advanced Threat Management. Platform enables companies to move from traditional risk management to threat-driven decision-making, leveraging real-time cyber intelligence for remediation actions [*].
Disadvantages
- Complex Licensing Structure. Per-app licensing model increases costs for cross-app business cases, while system complexity creates initial understanding challenges [*].
- Limited Customization Options. Lacks ability to deactivate unnecessary fields and needs improved cross-module data integration for metric-oriented dashboarding [*].
- Integration Challenges. Complex integration processes with internal tools lead to delayed build times despite available system connections [*].
Pricing
- Contact MetricStream for more information.
5. AuditBoard
AuditBoard is a cloud-based platform specializing in audit, risk, and compliance management. It provides a centralized platform where internal audit, risk, and compliance teams can manage their activities collaboratively. This includes tools for end-to-end audit management, from planning and fieldwork to reporting and follow-up.
AuditBoard also features a SOX compliance solution, simplifying the management of controls testing, documentation, and reporting, while its risk management tools help organizations identify, assess, and monitor risks in real time.
AuditBoard is particularly beneficial for medium to large enterprises and industries with stringent compliance requirements, such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing.
Top Features
- SOXHUB: A specialized feature for managing Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) compliance. It streamlines the process of documenting, testing, and certifying internal controls over financial reporting. It offers features such as control mapping, testing workflows, and certification processes.
- OpsAudit. Focuses on operational audits, providing tools to plan, execute, and report on audits across various business processes.
- AuditBoard AI. Leverages artificial intelligence, including generative AI, machine learning, and natural language processing, to automate workflows, surface key insights, and manage risks more efficiently.
- CrossComply. A compliance management solution that automates evidence collection, integrates assessment processes, and provides a centralized location for managing compliance controls.
- RiskOversight. Enables organizations to visualize and address risks across the enterprise by mapping complex parent/child relationships within risk categories and aggregating risk scores for a comprehensive view of risk health.
Advantages
- Enhanced Efficiency Tools. Significantly improves audit efficiency through user-friendly interface and seamless handling of complex tasks like planning, risk assessments, and tracking [*].
- Comprehensive Support System. Offers extensive support through regular webinars, office hours, help center resources, and an active community, alongside customizable modules for team-specific needs [*].
- Strong Implementation Impact. Delivers noticeable company-wide improvements, especially in issue action plan responsiveness, with continuous process enhancement through regular updates [*].
Disadvantages
- Workflow Limitations. Lacks time-saving features like work step copying, requiring manual creation of repetitive elements during field work [*].
- Inconsistent Feature Implementation. Cross-program changes and patches can create confusion and inefficiencies across different modules [*].
- Complex Permission Structure. Administrator-level permission management is complicated, requiring careful understanding of teams versus roles, while frequent feature releases can confuse users [*].
Pricing
- Contact AuditBoard for more information.
6. SAI360
SAI360 provides a centralized platform for managing GRC activities, allowing organizations to streamline risk assessments, automate compliance monitoring, manage audits, and track third-party risk.
Its integrated approach helps organizations identify, assess, and mitigate risks in real-time while ensuring compliance with industry regulations and internal policies.
SAI360’s configurable dashboards and analytics tools provide detailed insights into risk exposure, compliance status, audit findings, and incident data, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions and improve GRC performance.
The platform also supports health, safety, and environment (HSE) management, helping organizations meet workplace safety standards, track incidents, and promote a safe and compliant work environment.
Top Features
- Smart EHS&S. Integrates safety and sustainability features, enabling organizations to manage contractor safety and evaluate performance effectively.
- Operational Risk and Vendor Intelligence Dashboards. Provides real-time insights into vendor performance, including issue resolution speed, incident tracking, contract renewals, and operational resilience.
- Solution Configurability. Features an extensible data model with configurable user interfaces, forms, fields, and relationships, allowing organizations to tailor solutions to their specific needs.
- Learning and Best Practice Content. Includes preloaded frameworks, control libraries, and regulatory content, along with values-based ethics and compliance learning materials to support organizational training and development.
- AI Audit Assistant. Utilizes advanced artificial intelligence to automate the processing and analysis of audit evidence, accelerating workflows and ensuring accuracy without manual intervention.
Advantages
- Customizable Modules. Enables building separate workflows within each module to precisely meet organizational needs [*].
- Efficient Audit Management. Streamlines RAC audits with easy data collection and reporting capabilities [*].
- Strong Compliance Features. Particularly effective in cloud environment compliance, with organized policy management and robust audit trail capabilities [*].
Disadvantages
- Configuration Tool Limitations. Lacks advanced tools for environment migration, user rights management, and data archiving, with limited Microsoft Office integration for on-premises clients [*].
- Complex Module Understanding. Users face difficulties understanding module builds and maximizing application potential due to complicated structure [*].
- Contract Process Issues. Initial contract process is cumbersome and problematic. In fact, a user complained of the lengthy back and forth process to get an NDA [*].
Pricing
- Contact SAI360 for more information.
7. Onspring
Onspring is a no-code GRC software built on a flexible data model that enables custom application development for risk management, compliance, audit, and vendor management processes. The system’s core architecture supports dynamic risk scoring, automated workflows, and configurable assessment frameworks without requiring programming knowledge.
Onspring also handles automated control testing, compliance monitoring with rule-based alerts, incident tracking with SLA management, and centralized document management with version control.
The platform also provides real-time reporting capabilities, SAML 2.0 authentication, and RESTful APIs for enterprise system integrations with tools like SAP, ServiceNow, and Jira.
Each module can be customized through drag-and-drop interfaces while maintaining data relationships and audit trails across the platform.
Top Features
- Integrated Risk Management. Offers a centralized risk register to document and assess risks across the organization. It supports automated risk assessments, prioritization of risk analyses, and tracking of mitigation efforts.
- Compliance Management Automation. Integrates control libraries and maps them to various regulations and frameworks, such as ISO, NIST, and CMMC. It automates compliance testing, issue management, and reporting to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Policy Management. Includes a comprehensive policy portal for authoring, distributing, and managing policies. It facilitates policy attestations, exception tracking, and ensures that employees have access to the latest policies and procedures.
- Third-Party Risk Management. helps organizations assess, tier, and track vendors by integrating criticality ratings from cyber and financial monitoring services. It enables onboarding of new vendors, management of assessments, and tracking of mitigations to minimize third-party risks.
- Continuity and Recovery Planning. Assists in linking Business Impact Analysis (BIAs), automating testing, and activating continuity plans.
Advantages
- Scalable Functionality. Offers better flexibility in complexity levels, supporting various daily processes from simple to complex operations [*].
- Exceptional Customization & Support. Platform offers high customizability without IT dependency, backed by comprehensive training options and dedicated customer support representatives [*].
- Strong Integration Features. Excels in connecting and integrating applications, with simple app creation and Excel compatibility [*].
Disadvantages
- Change Management Challenges. Difficulty in locating and accessing change options, combined with expensive user licensing [*].
- Cross-Platform Data Access Issues. Limited references between apps create challenges in accessing data across different platform sections [*].
- System Timeout & Delegation Problems. Issues with timeout function reliability and delegation system requiring manual email updates rather than automatic recipient adjustments [*].
Pricing
- Contact Onspring for more information.
8. IBM OpenPages
IBM OpenPages is an AI-powered GRC platform that provides integrated risk management, regulatory compliance, operational resilience, and business continuity capabilities.
It leverages IBM Watson AI capabilities to operationalize risk management and regulatory compliance across all three lines of business, with zero end-user training required.
The system enables quick automation GRC processes within minutes through agile implementation workflows. Its core functionality includes embedded guidance for real-time user support, automated regulatory change management, and centralized risk monitoring.
Top Features
- External Loss Events Integration. Integrates with IBM FIRST Risk Case Studies, enabling users to consider industry-wide loss events and incorporate them into scenario analyses, assessments, and risk management, ensuring a broader risk perspective.
- Scenario Analysis. Leverages relevant system data to inform scenario workshops and identify scenarios requiring additional risk treatment, promoting proactive risk management.
- GRC Calculations. Automatically assigns values to fields based on object creation, updates, or associations, streamlining governance, risk, and compliance processes with precision.
- Watson Language Translator Integration. Detects and translates over 50 languages, ensuring content accessibility across language preferences set within OpenPages.
- IBM Cloud Pak for Data Cartridge. Provides flexible deployment across any cloud platform, integrating IBM and partner capabilities to accelerate AI-driven insights and GRC processes.
- IBM Watsonx Assistant. A virtual assistant offering 24/7 support for OpenPages users, answering common questions interactively and providing natural language search and direct links to specific pages or documents.
Advantages
- Powerful Analysis Capabilities. Effectively uses machine learning algorithms to understand context and identify patterns in large datasets with high precision [*].
- Robust Data Processing. Provides high-quality text analytics with metadata extraction capabilities and cloud deployment options for handling large data volumes [*].
- User-Friendly Implementation. Requires minimal special training with comprehensive documentation support, eliminating need for dedicated data engineers [*].
Disadvantages
- Cost Barriers. High pricing structure creates accessibility challenges for small businesses and individuals despite flexible pricing factors [*].
- Data Security Concerns. Cloud storage raises security concerns, with challenging tool integration and extensive training data requirements [*].
- Complex Reporting Tools. Cognos integration proves difficult for beginners, while access management features are powerful but overly complex [*].
- Accuracy Inconsistencies. Constrained knowledge base can lead to inaccurate results, particularly challenging given the high price point [*].
Pricing
- Contact IBM for more information.
9. LogicGate Risk Cloud
LogicGate Risk Cloud is another highly configurable no-code GRC platform that enables organizations to build and scale risk and compliance processes tailored to their unique needs.
Risk Cloud combines modular applications with a user-friendly, no-code interface, allowing teams to automate workflows, configure dashboards, and customize risk and compliance management without relying on extensive IT support.
Top Features
- Risk Cloud Quantify. Enhances traditional risk assessment techniques with Monte Carlo simulations, enabling organizations to quantify risk in financial terms and connect it to business impact.
- Pre-Built Applications. Provides over 20 pre-built applications tailored to specific GRC use cases, based on widely adopted standards and critical control frameworks.
- Third-Party Risk Management. Includes applications to assess and manage third-party risks, helping organizations evaluate vendor performance and tighten security.
Advantages
- Advanced Visual Reporting. Enables creation of distinctive visual reports with flexible customization of home screens and one-click report downloads [*].
- User-Friendly Customization. Offers intuitive interface suitable for all technical levels, allowing real-time regulatory compliance without IT dependency [*].
- Unified Access Platform. Provides single-pane-of-glass visibility with excellent implementation support and growing utilization potential [*].
- Integrated Security Overview. Enables comprehensive end-to-end security program visibility with quantifiable metrics across multiple modules [*].
Disadvantages
- Limited Risk Analysis Data. Absence of built-in loss data estimates requires manual customer input for risk analysis [*].
- Cost Concerns. Full module set implementation can become expensive [*].
- Testing Environment Absence. Lacks sandbox environment for testing changes before live implementation [*].
Pricing
- Contact LogicGate Risk Cloud for more information.
10. Archer Insight
Archer Insight centralizes risk information and uses advanced analytics to provide real-time insights into risk exposure. The platform uses a combination of risk scoring, scenario modeling, and quantitative analysis to enable organizations to anticipate the potential impact of various risk events.
Archer Insight also includes tools for tracking risk tolerance and supporting the decision-making process, making it easier for organizations to align their risk strategies with business objectives.
The platform provides visibility into key risk indicators (KRIs) and integrates with incident management, compliance, audit, and business continuity tools within the broader Archer IRM suite. This enables organizations to build a comprehensive risk management program, monitor risk trends over time, and implement actionable strategies to optimize risk resilience.
Top Features
- Risk Quantification Methodology. Offers a built-in quantitative risk assessment approach that replaces traditional qualitative methods, such as heat maps, with a series of straightforward questions. This methodology allows for the calculation of financial expected loss for quantitative risks.
- Archer Insight Workbench. Provides a dedicated tool for risk modeling and analysis, enabling users to conduct in-depth evaluations of various risk scenarios and their potential impacts on the organization.
- Control Specification Assessment. Allows for a detailed comparison of inherent, actual, and full states of a risk by specifying the control environment. This feature offers visibility into the effectiveness and value of each control in preventing risk occurrences or mitigating impacts.
- Quantitative Risk Aggregation. Enables the aggregation of risk exposures across various hierarchy structures, such as assets, regions, divisions, and functions, providing a comprehensive view of enterprise-wide risk.
- Visualization of Risk Uncertainty. Visualizes the full uncertainty around economic losses, leveraging common downside metrics like Value at Risk (VaR) and Conditional Value at Risk (CVaR). This visualization aids in understanding potential financial impacts under different risk scenarios.
- Risk Generator Application. Allows users to quickly generate multiple risk records based on selected risk statements and target applications, streamlining the process of risk identification and documentation.
Advantages
- Comprehensive Vendor Governance. Provides essential vendor risk management with methodical assessments, real-time monitoring, and customizable dashboards for quantified business risks [*].
- Customizable Workflow Management. Enables full control over vendor risk management program development with customized workflows for stakeholders [*].
- Extensive Vendor Management. Provides enterprise-wide management of vendor relationships, contacts, contracts, and risk exceptions with ongoing platform updates [*].
Disadvantages
- Cost and Update Issues. High licensing costs combined with infrequent upgrades and limited automation capabilities [*].
- Resource-Intensive Customization. Requires substantial resources including dedicated experts and consulting firms for custom dashboard creation and workflow implementation [*].
- Development Limitations. Difficult to develop custom applications beyond out-of-box solutions, with complications in managing large-scale application structures [*].
- Browser Compatibility Issue. Faces browser compatibility challenges requiring users to switch between different browsers, with poor user-friendliness requiring extensive customization [*].
Pricing
- Contact Archer Insight for more information.
11. ServiceNow
ServiceNow GRC is an integrated risk and compliance management platform built on the ServiceNow digital workflow foundation.
The platform unifies operational, IT, and enterprise risk management through automated workflows, while leveraging AI capabilities for continuous monitoring and control testing.
The system provides real-time risk scoring, automated policy management, and compliance tracking across multiple frameworks (SOX, GDPR, NIST).
Its core features include continuous control monitoring, vendor risk management, and automated issue remediation with configurable SLAs and built-in audit trails. ServiceNow also maintains a single data model that connects risks, controls, and business processes.
Top Features
- Integrated Risk Management. Provides a unified approach to identify, assess, and mitigate risks across the enterprise, ensuring alignment with business objectives.
- Policy and Compliance Management. Centralizes the creation, management, and distribution of policies and standards, automating compliance workflows to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Audit Management. Streamlines internal audit processes by automating audit planning, execution, and reporting, facilitating continuous monitoring and issue remediation.
- Third-Party Risk Management. Assesses and monitors risks associated with third-party vendors, ensuring that external partnerships do not compromise organizational security and compliance.
- 360° Relationship Visualization. Offers a visual representation of relationships between different types of critical data, such as controls, risks, and issues.
Advantages
- Centralized Management Excellence. Provides central management of risk, compliance, and governance processes with strong automation capabilities and real-time dashboard monitoring [*].
- ITIL Framework Integration. Offers complete ITIL framework implementation with easy-to-use compliance-based ITSM solution that adapts quickly within organizations [*].
- Comprehensive Core Solution. Delivers out-of-box functionality covering most process scenarios without requiring additional software deployment [*].
Disadvantages
- Process Adaptation Challenges. Requires significant upfront work to either adapt to ServiceNow’s methodology or customize the platform to existing processes [*].
- Implementation Constraints. Requires additional vendor support for deployment, with limited flexibility in custom solutions and poor performing pre built components [*].
- Template and UX Gaps. Lacks sufficient starter templates with need for user experience improvements and modernization updates [*].
Pricing
- Contact ServiceNow for more information.
12. LogicManager
LogicManager is a comprehensive Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) platform that integrates governance, risk management, and compliance activities into a centralized hub.
It uses taxonomy technology to connect risks across departments with controls, resources, processes, and personnel. This risk-based approach ensures proactive risk management while maintaining compliance through integrated monitoring and reporting capabilities.
LogicManager also provides role-based access controls, customizable assessment templates, and real-time reporting dashboards for stakeholder communication. In addition, it features a flexible architecture that supports various business functions through pre-built frameworks and configurable workflows.
Top Features
- One-Click Compliance. Reduces the effort and time required to satisfy compliance requirements by automating the mapping of controls to risks and compliance plans.
- Integration Hub. Offers a no-code, templated approach to connecting LogicManager with over 500 popular third-party applications.
- Centralized Risk Libraries. Offers pre-built, configurable libraries of industry-specific risks, controls, and assessment criteria, facilitating standardized data collection and risk assessments.
- Risk Maturity Model (RMM). Promotes a two-way conversation with the board, risk committees, and risk officers. It provides benchmarking KPIs against industry standards, actionable steps to improve the risk program, and reporting ready to deliver to the board.
- Outcome-Based Advisory Services. Offers dedicated advisory analysts who provide guided onboarding, support, and best-practice consulting. This partnership ensures that organizations receive the necessary guidance to achieve their risk management goals effectively.
Advantages
- Superior Customer Support. Provides excellent support team assistance with powerful TPRM capabilities and effective SME workflow management [*].
- Centralized Vendor Management. Delivers centralized vendor process management with no-code customization capabilities for real-time updates [*].
- Comprehensive Complaint Tracking. Excels in complaint management with customizable fields and detailed reporting capabilities [*].
Disadvantages
- Licensing Cost Barriers. User-based licensing model creates budget constraints for enterprise-wide deployment [*].
- Performance Issues. Slow report generation, limited task notification customization, and insufficient data tracking capabilities [*].
- Limited Discussion Features in Assessments. The absence of a feature for back-and-forth comments within risk and control self-assessments (RCSAs) limits detailed discussions, and the system’s three-level risk and control scale restricts more granular analysis [*].
Pricing
- Contact LogicManager for more information.
How to Choose the Right GRC Tool in 2026
Choosing the best governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) tool in 2026 comes down to aligning the platform with your size, risk profile, and existing tech stack. Use these criteria to narrow down your shortlist.
1. Map your use cases first
Identify the problems you want to solve:
- Centralizing audits and controls
- Reducing manual access reviews and identity risk
- Managing third-party and vendor risk
- Supporting specific frameworks such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, SOX, HIPAA, or GDPR
Document these use cases before you talk to vendors so you can evaluate features against real needs, not generic demos.
2. Look for unified identity and risk visibility
Modern GRC programs rely on accurate identity and access data. Prioritize tools that:
- Integrate deeply with your identity stack (SSO, directories, HRIS, SaaS, infrastructure)
- Provide a single view across human, non-human, and AI identities
- Support continuous monitoring rather than one-time assessments
3. Evaluate AI and automation, not just dashboards
In 2026, the best GRC tools do more than visualize risk. They help you:
- Automate access reviews, evidence collection, and control testing
- Surface noisy or high-risk permissions and toxic combinations
- Recommend remediation actions, not just show issues
Look for clear examples of where AI and automation reduce manual work in your own workflows.
4. Check integration depth, not just integration logos
Ask vendors to show:
- Entitlement-level visibility in your most important apps
- Bi-directional sync for provisioning and deprovisioning
- Support for custom and internal systems, not only popular SaaS
5. Validate implementation effort and ownership
Clarify:
- Typical implementation timelines for companies your size
- Who will own the platform day to day (security, compliance, IT, audit)
- How much configuration requires vendor services vs in-house admins
6. Compare total cost of ownership
Beyond licensing, factor in:
- Professional services and ongoing admin time
- Cost of manual work you can retire
Governance, Risk, & Compliance Tools (FAQs)
What is the difference between GRC and IGA?
GRC and Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) serve different but complementary roles.
- GRC tools focus on oversight and accountability: defining controls, managing risks, tracking compliance, and producing audit evidence.
- IGA tools enforce and govern access in real time: provisioning and deprovisioning access, running access reviews, enforcing least privilege, and integrating directly with SaaS apps, cloud platforms, and IdPs.
In practice, GRC defines what should happen. IGA ensures it actually happens.
Can a GRC tool replace an IGA platform?
No. GRC tools are not designed to manage or enforce identity access.
They typically lack:
- Deep integrations with SaaS applications, cloud services, and infrastructure
- Automated provisioning and deprovisioning
- Real-time access visibility
- Continuous access reviews or policy enforcement
GRC platforms document access controls. IGA platforms execute and enforce them.
Can a GRC tool replace my IdP?
No. Identity providers like Okta, Entra ID, or Google Workspace handle authentication and basic lifecycle events. They answer who can log in.
They do not:
- Govern access inside applications
- Run access reviews
- Enforce least privilege
- Provide audit-ready evidence of access decisions
IGA sits alongside the IdP to govern what authenticated identities can actually do.
Why do GRC-led access reviews break down at scale?
Traditional GRC-led access reviews rely on manual exports, spreadsheets, and quarterly certification cycles. As identity counts grow across SaaS apps, service accounts, and AI-driven workflows, this approach creates several problems:
- Reviews are outdated as soon as they start
- Reviewers approve access without context
- Remediation is slow or never completed
- Audit evidence reflects intent, not reality
This is why many teams move access reviews out of GRC tools and into purpose-built IGA platforms.
How should GRC and IGA work together?
The most effective programs connect GRC and IGA rather than forcing one to replace the other.
A modern approach looks like this:
- GRC defines risk, control objectives, and compliance requirements
- IGA enforces access policies, automates reviews, and generates evidence
- Audit-ready data flows back to GRC systems with minimal manual work
This reduces audit risk while dramatically lowering operational burden.
What should buyers look for beyond traditional GRC features?
For Director-level buyers, the differentiator is not policy management. It is execution.
Key capabilities to prioritize include:
- Real-time identity and access visibility
- Automated, continuous access reviews
- Native integrations with SaaS, cloud, and infrastructure tools
- Risk-based prioritization instead of blanket reviews
- Evidence that reflects actual access, not static snapshots
How do I know it is time to replace or supplement my current GRC tool?
You may need to modernize if:
- Access reviews still depend on spreadsheets or manual exports
- Identity and access data is incomplete or out of date
- Reviews take weeks and still lack confidence
- Teams bypass the system because it slows them down
- Audit prep creates recurring fire drills
If these issues sound familiar, it is often a sign that GRC alone is being asked to solve identity governance problems it was never built for, and that adding or replacing with a modern IGA platform is the next step.