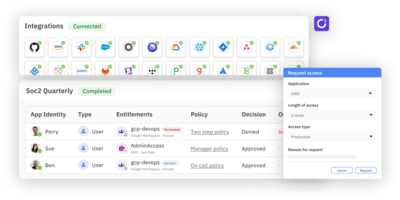
In cybersecurity, zero standing privileges (ZSP) refers to the principle of granting the minimum necessary level of access and privilege to a user or system to carry out specific tasks. This means that a user is only given the exact permissions and access required to perform their assigned duties, for only the amount of time they need it for, and nothing more.
How can you implement zero standing privileges?
Here are some steps to implement ZSP in your organization:
- Define roles and responsibilities: Start by defining the roles and responsibilities of each user in your organization. This will help determine the necessary level of access and privileges required for each user. You can take this a step further by creating an access control matrix that maps relevant access and permissions into those respective roles.
- Use policy-based access controls (PBAC): Implement policy-based access controls (PBAC) to grant users only the permissions they need to carry out their assigned duties through designated policies. PBAC allows you to define specific policies and assign permissions to the specific and necessary users, making it easy to control and manage user access.
- Use the principle of least privilege: Implement and enforce the principle of least privilege, which refers to an individual receiving just enough privilege, that is granted just-in-time, for only a limited time.
- Continuously monitor and review access: Continuously monitor and review the access and privileges granted to users to ensure that they are still in line with the defined roles and responsibilities. Automating these reviews can make it easy to send a notification or force a re-request for access that isn’t used after a certain number of days. This can help to identify and remediate any access control weaknesses or misconfigurations.
- Educate users: Educate users on the importance of following the principle of zero standing privileges and the consequences of misusing access and privileges. Make it easier on employees by holding training sessions, simplifying access requests to self service systems, or automating access controls.
By following these steps, you can implement ZSP in your organization and help to reduce the risk of security breaches.
Why is zero standing privileges needed in cybersecurity?
The concept of zero standing privileges is a crucial security principle as it helps to reduce the attack surface of a system and minimizes the potential impact of security breaches. Limiting the access and privileges of users and systems makes it more difficult for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities by stealing credentials. By following the principle of zero standing privileges, organizations can better protect their systems and data, and reduce the risk of security breaches and other malicious activities.
How do access controls implement zero standing privilege?
Access controls can implement ZSP by limiting the access and privileges of users and systems to the minimum necessary level required to perform their assigned duties.
There are several types of access controls that can be used to implement ZSP, including:
- Policy-based access controls (PBAC): PBAC allows organizations to manage access controls and grant privilege based on someone’s role and attributes in the organization, combined with policies. PBAC enforces policies on system users, letting these rules determine user access based on the role or attributes of the individual.
- Role-based access controls (RBAC): RBAC allows organizations to define specific roles and assign permissions, making it easy to control and manage user access. This helps to ensure that each user or system only has access to the resources and data that they need to perform their job, and nothing more.
- Discretionary access controls (DAC): DAC allows the owner of specific data to grant or revoke access to that data. This helps to ensure that access is only granted to those users or systems that need it, and that access is only granted for the minimum necessary time.
- Mandatory access controls (MAC): MAC is a type of access control that is based on security labels and categories. This type of access control is used to enforce the principle of least privilege and to ensure that users have access to the data they need to fulfill their requirements.
- Access control lists (ACLs): ACLs are used to specify which users or systems have access to a specific data, and what level of access they have. This helps to ensure that each user only has access to the data that they need to be successful in their duties.
By using these types of access controls, organizations can implement ZSP and increase their security measures through reducing the outstanding and unnecessary access that individuals may possess.
Summary
Zero standing privileges (ZSP) refers to the principle of granting the minimum necessary level of access and privilege to a user or system to carry out specific tasks. This principle is crucial to improving an organization’s security posture as it reduces the risk of security breaches. Zero standing privileges, closely related to the principle of least privilege, can be implemented in many ways most effectively through access reviews. Zero standing privileges helps organizations to reduce the risk of security breaches and ensure the safety of sensitive data.