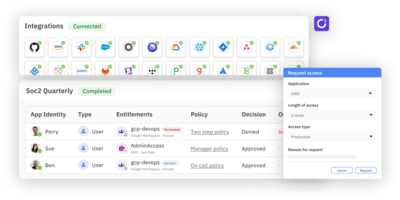
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud services, managing the permissions granted to both human and machine identities becomes crucial. CIEM tools provide granular visibility and control over these entitlements, ensuring that the right entities have the right access at the right times, and for the right reasons.
What is CIEM?
CIEM is a security solution designed to manage and secure identity and access entitlements in cloud environments.
The primary goal of every CIEM system is to minimize the risks associated with excessive permissions, misconfigurations, and identity sprawl, which can lead to security breaches.
💡Identity sprawl refers to the situation where an organization has many unused, outdated, or improperly managed user accounts and digital identities spread across its systems and applications.
What is the difference between CIEM and CNAPP?
CIEM (Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management) and CNAPP (Cloud Native Application Protection Platform) are both cloud security tools, but CIEM acts like a gatekeeper managing who (identities) can access what (resources) in the cloud, enforcing least privilege.
CNAPP offers a more comprehensive security suite specifically designed for cloud-native applications, incorporating CIEM’s functionalities alongside workload protection, vulnerability management, and other features for a holistic security approach.
While CIEM is ideal for managing identities across cloud platforms, CNAPP is more useful for securing cloud-native applications themselves.
How Does CIEM Work?
CIEM operates in six stages through a centralized model, ensuring tight control and visibility over entitlements across multiple cloud platforms. The system identifies excessive permissions, dormant accounts, and segregation-of-duty (SoD) violations by continuously analyzing permissions and usage patterns.
Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Stage 1: Data Collection
The initial stage involves a thorough scan of the cloud environment to collect detailed information on all the resources, users, and associated permissions.
CIEM tools integrate with various cloud services to extract data, ensuring coverage across environments like AWS (amazon web services), Azure, and Google Cloud. This comprehensive data collection is continuous, adapting to new resources and changes in the cloud infrastructure.
Stage 2: Entitlement Mapping
Upon gathering data, CIEM solutions construct a comprehensive map of all entitlements within the cloud infrastructure. This mapping details every permission, its scope, and its associations with particular users or groups.
The visualization of these entitlement maps helps in identifying over-privileged accounts, dormant accounts, and deviations from standard practices, which are critical for tightening security measures.
Stage 3: Security Policy Enforcement
With a clear map of entitlements, CIEM systems enforce predefined security policies. These policies are tailored to uphold the principle of least privilege (PoLP), ensuring that users and applications have no more access than necessary to perform their tasks.
Policy enforcement can be automated to react in real-time, such as revoking excessive permissions dynamically or restricting access based on the context of the request (e.g., location, time, or device used).
Stage 4: Continuous Monitoring & Alerting
CIEM platforms continuously monitor for unusual access patterns or deviations from typical user behavior. This proactive surveillance includes real-time analysis of transaction logs and access patterns, leveraging advanced analytics and machine learning to detect anomalies.
When a potential threat is detected, the system triggers alerts, enabling rapid response to potential breaches or policy violations.
Stage 5: Automatic Remediation
Advanced CIEM solutions include automated remediation capabilities. These features allow the system to act autonomously to correct risky entitlements.
For example, if an account is found to have unnecessary permissions, the system can automatically adjust these to align with security policies. Likewise, temporary permissions can be granted for specific tasks and revoked immediately upon task completion, minimizing the window of exposure.
Stage 6: Compliance Reporting
Finally, CIEM aids in regulatory compliance by generating detailed reports that document the entitlement and the enforcement of security policies. These reports are critical during audits, providing verifiable proof that the cloud environment adheres to internal security standards and external regulatory requirements.
By simplifying the reporting process, CIEM also helps organizations maintain continuous compliance with less manual effort.
The Main Components of CIEM
The CIEM framework is designed to enhance cloud security by managing and securing complex entitlements and access controls. It leverages several key components to offer comprehensive security for cloud environments.
Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM)
The architecture of CIEM is based on the underlying principles of IAM. Only difference is, CIEM enhances the ‘traditional IAM’ through precise definition of access rights of users and applications over cloud resources.
It details what resources can be accessed and what actions can be performed (e.g., read, write, delete). This granularity ensures that only authorized entities have access, effectively reducing the potential attack surface.
Principle of Least Privilege Access
CIEM applies the principle of least privilege by continuously analyzing user permissions and access rights. In this case, configuration of systems and applications to grant the least privilege from the outset.
New accounts are created with minimal access rights, with additional privileges provided only after a thorough review and approval process.
Key actions include:
- Enforcement of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). CIEM systems may enforce least privilege by assigning roles to users based on their job functions. These roles are equipped with permissions that strictly align with the user’s responsibilities, ensuring that no additional privileges are granted beyond what is necessary for their tasks.
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Privileges. CIEM may implement JIT access controls, which temporarily elevate a user’s privileges for a specific task and then revert to the baseline after the task is completed. This limits the exposure time of elevated privileges and reduces the risk of abuse.
- Granular Permissions Management. By dividing cloud resources into smaller, more controlled segments, CIEM allows for more granular permission settings. This prevents lateral movement within the network, as each segment can have tailored access policies that strictly enforce least privilege.
Related → What Is Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)?
Visibility and Auditing
Traditional security measures often fail to provide a centralized view of entitlements across various cloud platforms. CIEM addresses this gap through:
- Entitlement Discovery and Mapping. Automatic scans that identify and map all entitlements, providing a comprehensive overview of access rights and policies.
- Continuous Monitoring. Real-time monitoring of user activities and access patterns to promptly detect and react to abnormal behavior or potential security threats.
- Audit Trails. Detailed logging of user activities and access attempts, which are crucial for forensic investigations and compliance audits.
Policy Enforcement
When combined with an identity governance system (IGA), CIEM can help enable the precise definition and enforcement of access policies tailored to various organizational needs, based on:
- User Roles. Access rights are associated with specific job functions, ensuring users receive appropriate permissions.
- Geographical Restrictions. Access can be controlled based on the user’s location, aiding compliance with regional data privacy laws.
- Temporal Restrictions. Access can be restricted during sensitive times or off-hours to enhance security.
- Device-Based Restrictions. Access can be restricted to approved devices, mitigating risks from potentially compromised hardware.
Automated Remediation
Advanced CIEM systems can identify and also rectify security issues through automated remediation, which includes:
- Corrective Action Recommendations. CIEM proposes specific steps to address vulnerabilities, enhancing security posture.
- Guided Remediation Workflows. CIEM aids security teams by outlining effective remediation strategies, simplifying the resolution of security issues.
- Compliance Assistance. CIEM supports compliance with various regulatory standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA) by ensuring that access management practices are both visible and auditable. It also logs all actions taken, providing an audit trail that is vital for compliance reporting and post-incident analysis.
Privileged Access Management (PAM) or Just-in-Time Access (JIT)
PAM and JIT systems focus on securing privileged accounts that have high levels of access within your IT infrastructure. CIEM integrates with PAM and JIT solutions by providing valuable insights into cloud entitlements. This allows the PAM and JIT systems to:
- Identify Risky Behaviors. CIEM can flag unusual access patterns or attempts to access unauthorized resources from privileged accounts, potentially indicating a compromised account.
- Remediate Potential Compromise. By correlating data with the systems, CIEM can help identify and take swift action to mitigate potential breaches involving privileged accounts.
Related → What is Just-in-Time Access (JIT)
CIEM Use Cases/Application
Complex Cloud Environments
💡Scenario → An organization with a complex cloud environment, utilizing multiple cloud service providers and a wide array of cloud resources.
Benefits: CIEM provides detailed visibility and control over cloud entitlements across multiple platforms, ensuring consistent policy enforcement and reducing the risk of over-permissioned identities. It helps manage the complexity of multi-cloud environments by offering a unified approach to entitlement management.
Strict Compliance Requirements
💡Scenario → An organization operating in a highly regulated industry with strict compliance requirements, such as financial services, healthcare, or government.
Benefits: CIEM solutions offer advanced compliance monitoring and reporting capabilities tailored to cloud environments. They help ensure adherence to regulatory standards by continuously monitoring entitlements, providing audit trails, and automating access reviews and certifications.
Dynamic and Scalable Cloud Workloads
💡Scenario → An organization with dynamic and scalable cloud workloads that require frequent changes to access permissions and entitlements.
Benefits: CIEM solutions provide automated entitlement management, enabling organizations to rightsize permissions in response to changing workloads. This automation reduces administrative overhead, ensures timely updates, and maintains security and compliance in fast-paced cloud environments.
Adoption of DevOps and Agile Methodologies
💡Scenario → An organization adopting DevOps and Agile methodologies, requiring rapid provisioning and deprovisioning of cloud resources.
Benefits: CIEM supports the agility and speed required by DevOps practices by automating entitlement management and integrating with CI/CD pipelines. This ensures that access permissions are appropriately managed throughout the development lifecycle, reducing the risk of security gaps.
Enhanced Security Posture
💡Scenario → An organization looking to enhance its overall security posture by minimizing the attack surface and reducing the risk of privilege escalation.
Benefits: CIEM focuses on enforcing the principle of least privilege, continuously monitoring entitlements, and detecting anomalies in access patterns. This approach helps identify and mitigate potential security threats before they can be exploited, improving the organization’s overall security posture.
Resource Optimization and Cost Management
💡Scenario → An organization aiming to optimize resource usage and manage cloud costs effectively.
Benefits: CIEM solutions provide insights into resource entitlements and usage patterns, helping organizations identify and eliminate unnecessary permissions. By optimizing entitlements, organizations can reduce the risk of resource sprawl, improve efficiency, and manage cloud costs more effectively.
CIEM vs SIEM vs CSPM: What is the Difference?
Feature / Aspect | CIEM | SIEM | CSPM |
Primary Focus | Manages and secures identity and access in cloud environments. | Monitors and analyzes security events and logs across the network. | Manages and secures cloud infrastructure configurations. |
Core Functionality | Minimizes excessive cloud permissions and enforces least privilege. | Aggregates and correlates log data to detect and respond to threats. | Scans cloud configurations for misconfigurations and compliance. |
Key Components | Identity governance integration, rights visibility, and access analysis. | Log collection, event correlation, real-time alerting. | Configuration audits, compliance monitoring. |
Data Handling | Works with identity and access data. | Processes all types of log and event data. | Deals with configuration and metadata. |
Security Focus | Targets insider threats and manages identity-based access risks. | Provides broad security coverage, detecting both insider and external threats by analyzing activity. | Aims to prevent configuration errors and enforce compliance standards to mitigate cloud vulnerabilities. |
Use Cases | Managing least privilege policies, monitoring unusual access patterns, and automating permission adjustments. | Real-time security monitoring, incident response, forensic analysis, and compliance reporting. | Compliance audits, risk assessment reports, real-time compliance fixes, and historical analysis for security improvements. |
Integration | Often integrates with cloud access security brokers (CASBs), identity providers (IdPs), identity governance (IGA), and cloud IAM (Identity and Access Management) services. | Integrates with existing network infrastructure, endpoint protection platforms, and other security tools. | Typically integrates with cloud service providers (CSPs) directly, leveraging native APIs for configuration data. |
Deployment | Deployed as part of a broader cloud security strategy, often in conjunction with CSPM, IGA, PAM, JIT, and other cloud-native security solutions. | Can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud; often requires significant resources for data storage and processing. | Cloud-native, with automatic scaling to match the cloud environment's size and complexity. |
Outcome | Enhanced control over who can access what resources in the cloud, reducing the risk of data breaches due to over-privileged accounts. | Improved detection of and response to security incidents, with comprehensive coverage across all network activity. | Ensures that cloud environments adhere to security best practices and compliance requirements, reducing the risk of misconfigurations. |
CIEM vs SIEM
Security Information and Event Management systems are designed to provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s information security. They collect and aggregate log data generated throughout the organization’s technology infrastructure, from host systems and applications to network and security devices such as firewalls and antivirus filters.
CIEM solutions, on the other hand, are more specialized tools focused specifically on managing identities and entitlements in cloud environments. As organizations migrate to the cloud and adopt multi-cloud strategies, rightsizing permissions and entitlements efficiently and securely becomes a challenge.
💡While SIEM is essential for overall security incident management and real-time alerting across both on-premises and cloud environments, CIEM is specifically tailored for cloud security management focusing on identity security and access controls.
CIEM deals primarily with the who (identities) and what (permissions) in a cloud context, whereas SIEM is concerned with the when (real-time threat detection) and how (attack methods and pathways).
CIEM vs CSPM
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools are designed to help organizations automate the identification and remediation of risks associated with their cloud environments. These tools focus on ensuring that cloud deployments are secure and compliant with various regulations and best practices.
Meanwhile, CIEM solutions help enterprises manage the complexity of their permissions across the cloud environments — particularly during expansion.
💡The primary distinction between CIEM and CSPM lies in their focus areas:
- CIEM is deeply focused on identity and access management, ensuring that every identity in the cloud has the appropriate level of access rights based on their role and responsibilities.
- CSPM, meanwhile, offers a broader view of cloud infrastructure security, focusing on configurations, compliance, and overall infrastructure security posture.
In practice, CIEM and CSPM are complementary technologies. CIEM addresses who can do what within a cloud environment, while CSPM ensures that the environment itself is set up securely and remains compliant with various regulations and best practices.
What are the Key Benefits of CIEM?
Reduced Security Risks
In cloud environments, things change rapidly, making it easy for permissions to grow out of control.
With CIEM, you can tighten up these permissions by following the principle of least privilege. This means each user or application only gets access to the resources absolutely necessary for their tasks. By minimizing these permissions, you greatly reduce the risk of damage from insider threats.
Improved Visibility
Using the typical traditional methods to track who has access to what across different cloud platforms can be a headache.
CIEM solves this by giving you a centralized dashboard that shows all user permissions and activities. This visibility helps you quickly spot any excessive or outdated permissions that could pose a security risk. You’ll also have the capability to audit and review access patterns over time, which can help identify unusual behaviors or policy violations.
Enhanced Compliance
Keeping up with data security regulations can be tough, but CIEM makes it easier. It helps you enforce the access controls required by laws like GDPR or HIPAA, ensuring you’re always compliant.
Plus, CIEM can automatically generate detailed reports that prove your compliance, making audits a breeze. This function is crucial for industries where data security is vital, as it reduces the risk of costly fines and protects against reputational damage.
Faster Incident Response
If a security breach happens, CIEM helps you act fast. It quickly shows you which accounts are compromised and how extensive the unauthorized access is.
This allows you to contain the breach quickly and reduce the damage, helping protect both your sensitive data and your reputation. The system can also integrate with other security tools to automate responses to common threats, further reducing the time to react.
Streamlined Workflows
CIEM automates many routine tasks, like setting up or revoking access, which traditionally take up a lot of your IT team’s time. This automation ensures your access settings are always up-to-date and reduces the chance of human error. Your security team can then focus more on strategic tasks that improve your security stance.
Additionally, automated workflows can be customized to fit the unique needs of your organization, enhancing efficiency across various departments.
DevOps Security
CIEM fits perfectly into DevOps practices, securing the rapid setup of infrastructure without slowing down operations. It ensures that security measures keep up with the fast pace of development, integrating security into your workflows without hindering agility.
Moreover, CIEM supports continuous integration and deployment cycles, allowing security and compliance checks to occur at every phase of development, which helps in early detection of potential security issues.
What Challenges Does CIEM Help Address?
Excessive Privileges
For most organizations promoting, onboarding and offboarding employees, it’s quite common for users to accumulate more permissions than required, increasing the risk of security breaches.
CIEM tools help with these by identifying and removing these unnecessary privileges. It minimizes the permissions footprint, significantly reducing the potential attack surface, — this way, limiting the damage a breach can inflict.
Visibility Across Multi-Cloud Environments
As organizations increasingly adopt multi-cloud strategies, managing security across various platforms becomes more challenging. CIEM provides a unified view of all cloud permissions, regardless of the cloud service provider.
This centralized visibility is key to understanding and managing your overall cloud security posture, helping you spot vulnerabilities and inconsistencies across different platforms.
Shadow IT and Unmanaged Resources
Shadow IT—where employees use cloud services without IT approval—creates significant security blind spots.
CIEM addresses this challenge by providing tools to discover and manage unregulated cloud resources. It integrates these resources into the organization’s overall security framework, extending protection to all cloud assets and reducing the risks associated with unsanctioned IT activities.
Scalability and Elasticity of Cloud Services
The dynamic nature of cloud services, where resources are continuously scaled up or down, poses significant challenges for access management. CIEM solutions excel in such environments by offering dynamic permissions management.
They can automatically adjust access rights based on real-time changes in the cloud infrastructure, such as auto-scaling events or deployment of new services. This ensures that security measures keep pace with the rapid changes of the cloud environment, maintaining consistent protection and compliance.
Blind Spots from Non-Human Identities
CIEM also extends its capabilities to non-human identities such as bots, service accounts, and automated processes. These identities often have significant access but are overlooked by traditional security systems.
CIEM ensures these machine identities are properly managed and monitored, reducing the risk of them becoming a gateway for attackers.
Unused or Dormant Identities
Over time, certain user accounts may no longer be needed but remain active within the system, posing a silent security threat. CIEM helps in identifying such dormant or unnecessary identities and facilitates their safe removal.
This not only cleans up your system but also tightens security by eliminating potential entry points for attackers.
Privilege Escalation and Lateral Movement
Attackers often exploit permissions to escalate their access levels or move laterally across the network. CIEM employs advanced detection mechanisms to monitor for unusual access patterns or changes in behavior that may signal attempts at privilege escalation or lateral movement. This early detection is vital for preventing attackers from gaining further foothold within your infrastructure.
Third-Party Access Management
Managing access for third-party vendors is particularly challenging due to the nature of the access they require. CIEM solutions provide robust tools to oversee and control these third-party entitlements effectively.
By ensuring that vendors have access only to what is strictly necessary, CIEM reduces the risk of breaches originating from compromised third-party systems.
VIEW, MANAGE, AND PROTECT ENTITLEMENTS ACROSS YOUR CLOUD PLATFORMS AND DATA WAREHOUSES —
All with ConductorOne — Start Now 👈.
The Role of CIEM in Cloud Security: How Does It Improve Cloud Security?
CIEM is essential in the security architecture of modern cloud environments. It primarily addresses the complexities and risks associated with managing identities and entitlements across different cloud platforms.
Traditionally, managing these permissions has been riddled with limitations:
- Limited Visibility. Traditional cloud provider IAM tools often have significant visibility gaps, particularly with entitlements that are assigned outside of their native management frameworks, such as those in Kubernetes environments. These tools are generally designed to manage permissions within a single framework, leaving blind spots in external systems or custom configurations.
- Fragmented Management. Organizations operating across multiple cloud platforms face substantial challenges in tracking and managing entitlements consistently. Each cloud platform often has its own set of tools and processes for managing access, leading to a fragmented approach that can easily result in oversights and vulnerabilities.
To solve these challenges and help organizations mitigate data risks associated with data breaches, unauthorized access, and compliance violations, CIEM integrates and enhances the cloud security framework:
- Automated Real-Time Policy Enforcement. Advanced CIEM solutions leverage real-time policy enforcement mechanisms. These mechanisms automatically detect and react to changes in the cloud environment, such as the creation of new resources or modification of existing ones. By continuously validating permissions against predefined policies and current contextual information, CIEM tools prevent privilege escalation and reduce the attack surface available to potential threats.
- Anomaly Detection and Remediation. Through advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms, CIEM systems identify anomalous behavior related to identity usage and permissions. This includes detecting unusual access patterns or unexpected escalation of privileges, which could indicate a breach or an insider threat. Once an anomaly is detected, CIEM solutions can trigger automated workflows to remediate the issue, such as revoking the suspicious permissions or alerting security teams for further investigation.
- Identity and Access Granularity. CIEM tools provide granular visibility and control over identities, whether they pertain to humans, services, or machine identities. By precisely defining and enforcing entitlements, CIEM ensures that each identity has just the right level of access required to perform its functions. This granularity extends across multi-cloud environments, simplifying the management of permissions in complex scenarios where different cloud providers may have disparate IAM models.
- Scalable Management of Identity Lifecycles. In large-scale cloud environments, managing the lifecycle of identities and their corresponding entitlements can become overwhelming. CIEM solutions automate key processes such as provisioning, modification, and de-provisioning of access rights. This reduces administrative overhead, minimizing the risk of lingering access rights that could potentially be exploited.
VIEW, MANAGE, AND PROTECT ENTITLEMENTS ACROSS YOUR CLOUD PLATFORMS AND DATA WAREHOUSES —
All with ConductorOne — Start Now 👈.
How to Implement CIEM [A Step-by-Step Checklist]
- Assess Current Infrastructure
- Set Goals and Objectives
- Select a CIEM Solution
- Set up the CIEM
- Train and Onboard Users
- Create an Ongoing Management and Review Process
Assess Current Infrastructure
- Conduct a thorough inventory of your existing cloud resources, including all cloud service providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, etc.), virtual machines, databases, storage accounts, and applications.
- Use automated discovery tools to ensure no resources are overlooked.
- Begin by cataloging all assets within your cloud environments, including virtual machines, storage buckets, databases, and services.
- Understand and document the minimum necessary access for each role within your organization. This includes identifying which resources each role needs access to and what type of actions they need to be able to perform.
- Review compliance requirements relevant to your industry. Determine how CIEM can help meet these standards by controlling and monitoring access.
Set Goals and Objectives
- Establish clear and measurable goals for the CIEM implementation. Objectives may include reducing the risk of unauthorized access, improving compliance, automating entitlement management, or enhancing visibility into cloud permissions.
- Define KPIs and metrics to measure the success of the CIEM deployment. Common KPIs include the number of over-permissioned identities reduced, compliance audit scores, and the time taken to detect and remediate entitlement anomalies.
Select a CIEM Solution
- Compare different cloud security solutions based on features such as real-time monitoring, policy management, risk assessment capabilities, and integration with existing security tools.
- Evaluate vendors on their stability, customer support, scalability, and the integrations they offer with existing cloud providers and cybersecurity solutions.
- Conduct a pilot project with shortlisted CIEM solutions to evaluate their effectiveness in your environment.
Set up the CIEM
- Integrate the CIEM solution with your cloud environments. This typically involves configuring the CIEM to access cloud APIs and ingest logs and configuration data.
- The CIEM solution should discover and catalog all cloud resources, permissions, and entitlements.
- If deploying alongside an identity governance (IGA), just-in-time access (JIT), privileged access management (PAM) solution, use CIEM context to discover overprivileged or anomalous access rights and implement policy and access changes. This will ultimately help on the path to least privilege access..
- Set up automated workflows to respond to detected anomalies or policy violations, such as revoking user access, alerting administrators, or initiating remediation processes.
Train and Onboard Users
- Educate users on the importance of CIEM and their roles in maintaining cloud security. This includes training on how to use the CIEM system effectively. Also ensure they understand their entitlements and the importance of compliance with security policies.
Create an Ongoing Management and Review Process
- Regularly review access rights and entitlements to ensure they remain aligned with user roles and business requirements. Adjust policies as necessary.
- Use the CIEM’s monitoring capabilities to continuously track access patterns and detect anomalies. Set up alerts for unusual activities that could indicate a security risk.
As your cloud environment and business needs evolve, regularly update your CIEM policies and configurations to adapt to new services, and assets.
Secure Your Cloud Infrastructure from One Control Plane — with ConductorOne
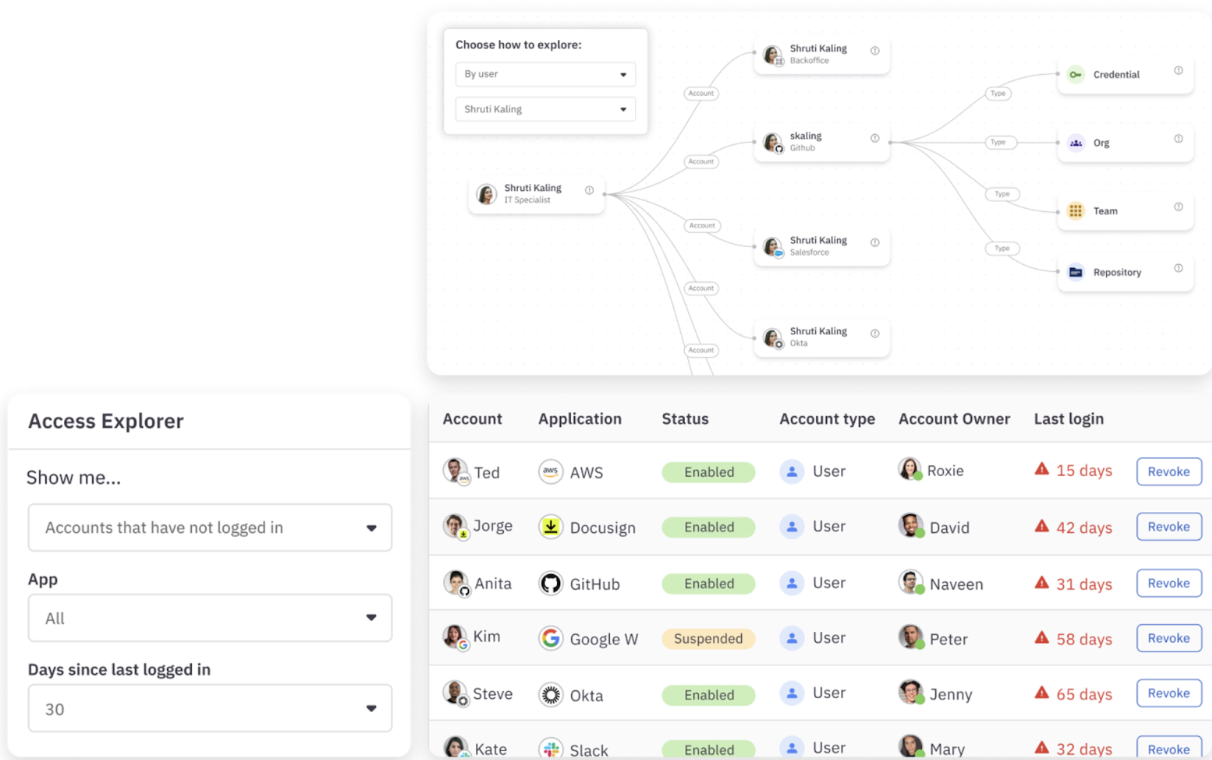
Choosing ConductorOne as your preferred CIEM solution reduces the complexities involved in access controls, ensuring that access rights are precisely aligned with user roles and responsibilities. Its CIEM solution offers a layered security approach for organizations looking to secure their cloud environments against unauthorized access and streamline their security operations.
Furthermore, ConductorOne’s CIEM capabilities are built on a foundation of advanced technology that allows for dynamic permission adjustments based on user activity and risk assessments. This ensures that security measures evolve in real-time, keeping pace with potential threats.
But don’t take it from us— rather, take it from Ramp, a finance automation company — whose mission is to help businesses save time and money:
💡Case Study → How Ramp Implemented Least Privilege Access
Why Do Companies Like Ramp Choose ConductorOne?
- Automated Permission Management. ConductorOne simplifies the complex task of permission management. Its automation capabilities allow for real-time adjustments and optimizations, reducing manual overhead and minimizing the risk of human error.
- Comprehensive Visibility. Gain a clear, unified view of all entitlements across your cloud environment. ConductorOne’s dashboard provides detailed insights into who has access to what, making it easier to audit and comply with regulatory requirements.
- Least Privilege Enforcement. ConductorOne excels in enforcing the principle of least privilege, a critical security posture that grants users only the access necessary to perform their tasks. This minimizes potential attack surfaces and reduces the risk of internal threats.
- Scalable Architecture. Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, ConductorOne scales seamlessly with your needs. Its flexible architecture ensures that as your business grows, your CIEM capabilities can grow with it without compromising performance.
- Integration-Friendly. ConductorOne integrates smoothly with existing IT and security ecosystems, including popular cloud platforms and identity providers. This compatibility ensures that you can leverage its benefits without major overhauls to your current systems.
VIEW, MANAGE, AND PROTECT ENTITLEMENTS ACROSS YOUR CLOUD PLATFORMS AND DATA WAREHOUSES —
All with ConductorOne — Start Now 👈.