Manage external data sources
What are external data sources?
External data sources are S3 buckets and other file systems that ConductorOne has the permissions to read and write. External data sources can be used for:
- Pushing audit logs for offline storage
- Pushing audit logs for consumption into your SIEM
- Ingesting application data
Set up an S3 data source
This task requires the Super Administrator role in ConductorOne and the ability to create an IAM Role in AWS.
ConductorOne uses an IAM Trust relationship between your AWS Account and ConductorOne’s Service AWS Account for integrating to S3. This is the AWS-recommended method of sharing access to AWS Accounts. ConductorOne has a specially created and isolated AWS Account dedicated to the AWS integration.
Step 1: Get a ConductorOne-provided External ID for the AWS IAM Role
Log into ConductorOne.
In the navigation panel, open Admin and click Settings.
On the External data sources tab, click Add data source.
Choose who will own and manage this integration, then click Create and add details.
The S3 bucket integration form opens. Copy and save the External ID generated for you by ConductorOne. You’ll use this value in Step 2.
Step 2: Create an AWS IAM Role for ConductorOne
In a new browser tab, navigate to AWS and sign into your AWS account.
Navigate to the Identity and Access Management (IAM) dashboard.
Click Roles > Create Role.
Select Custom Trust Policy and paste the following code into the Trust Policy JSON editor, replacing
<EXTERNAL ID FROM C1>with the value you saved in Step 1.{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::765656841499:role/ConductorOneS3DatasourceService" }, "Action": "sts:AssumeRole", "Condition": { "StringEquals": { "sts:ExternalId": "<EXTERNAL ID FROM C1>" } } } ] }Click Next.
Do not make any changes on the Add permissions page. Click Next.
On the Name, review, and create page, in the Role Name field, enter ConductorOneIntegration.
Optional. Add any tags relevant to your organization.
Click Create role.
Step 3: Assign policy to ConductorOneIntegration AWS role
Back on the Roles page, click on the newly created ConductorOneIntegration role to view the role’s details.
Under Permissions Policies, click Add Permissions and select Create Inline Policy.
Click the JSON Editor tab and paste in the following code:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3:GetObject", "s3:GetObjectAttributes", "s3:HeadBucket", "s3:ListBucket", "s3:GetBucketLocation", "s3:PutObject" ], "Resource": [ "arn:aws:s3:::<BUCKET NAME>", "arn:aws:s3:::<BUCKET NAME>/*" ] } ] }
If you plan to only use this s3 bucket for application data syncs and therefore need only be read only, you can safely omit
"s3:PutObject"from the policy.
Click Review Policy.
In the Name field, enter ConductorOnePermissions.
Click Create policy.
Copy and save the Role ARN for the newly created policy. The Role ARN is formed as
arn:aws:iam::<UNIQUE STRING>:role/ConductorOneIntegration. You’ll use this value in Step 4.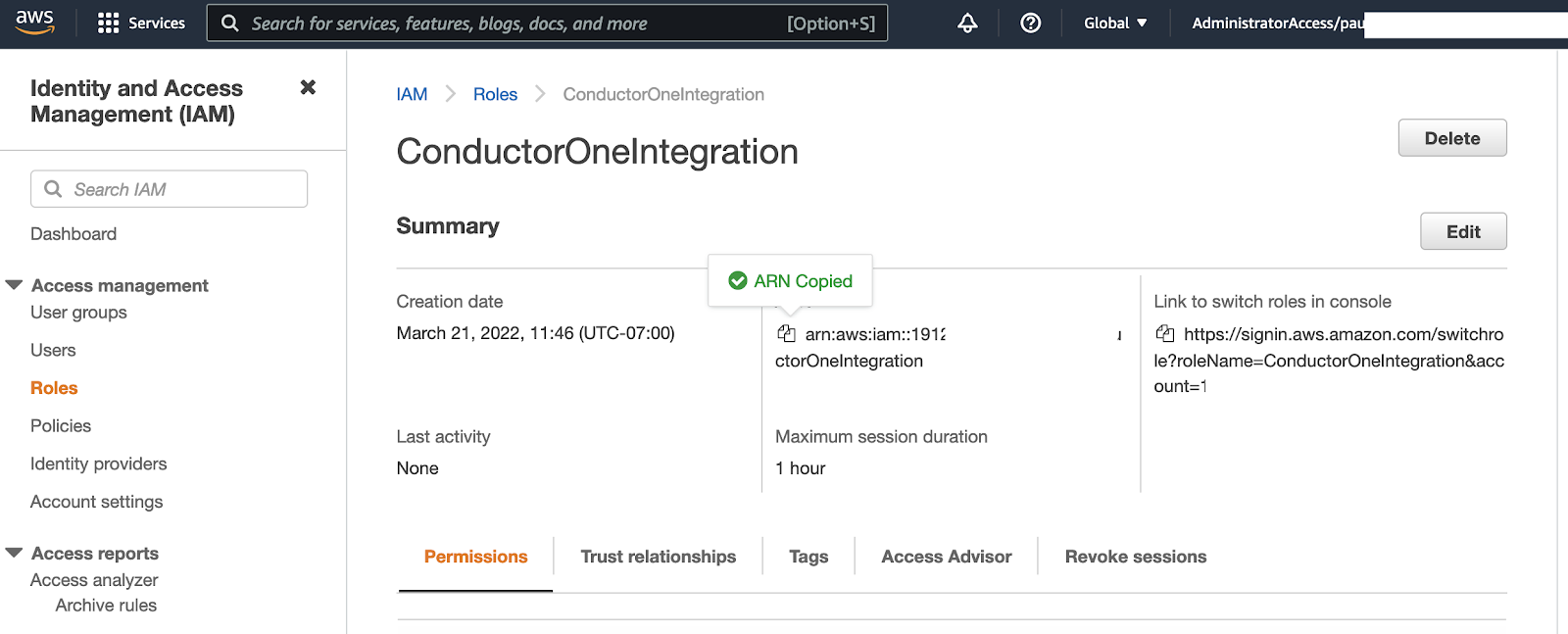
Step 4: Configure the external data source in ConductorOne
Return to the ConductorOne Settings > External data sources page if necessary and navigate to your newly created external data source.
Paste the Role ARN you generated in Step 2 into the Role ARN field.
Enter the name of the S3 bucket that contains the files you want to use in ConductorOne in the S3 bucket field.
Click Save.